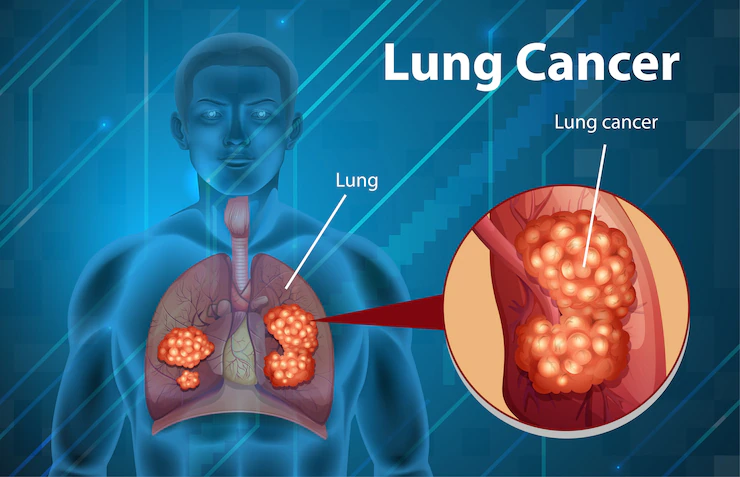
Lung Cancer (LC) may be a sort of cancer that starts within the lungs. Cancer starts when cells within the body begin to grow out of control.
Cancer cells develop because of multiple changes in their genes. These changes can have many possible causes.
Lifestyle habits, genes you get from your parents, and being exposed to cancer-causing agents in the environment can all play a role. Many times, there is no obvious cause.
Certain genes control a cell’s life cycle – growth, function, division, and death. When these genes are damaged, the balance between normal cell growth and death is lost.
Cancer cells are caused by DNA damage and out-of-control cell growth.
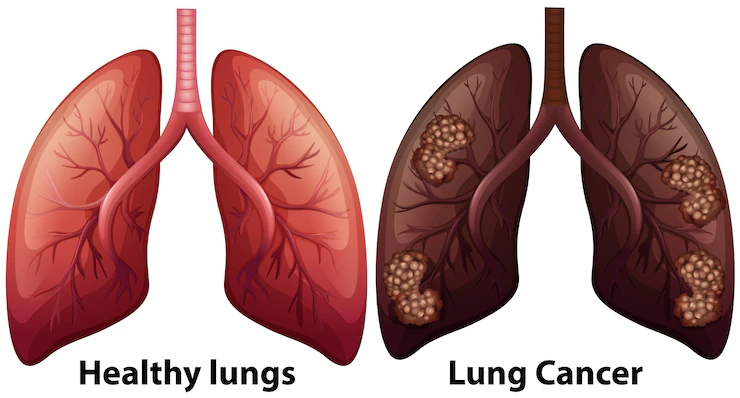
WHAT CAUSES LUNG CANCER?
SMOKING- Tobacco usage is by far the most common cause of LC. Around 80% of lung cancer fatalities are caused by smoking, and many more are caused by secondhand smoke exposure.
Although smoking is by far the most significant risk factor for LC, it frequently interacts with other factors.
Smokers are at a significantly greater risk, as are those who are exposed to other known risk factors like radon and asbestos. Because not everyone who smokes develops lung cancer, other factors such as genetics are likely to play a role.
CAUSES IN PEOPLE WHO DON’T SMOKE– Lung cancer does not affect everyone who smokes. Many patients with lung cancer have smoked in the past, while many others have never smoked.
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) can be diagnosed in people who have never smoked, but it does happen.
Exposure to radon, secondhand smoking, pollution, and other factors can cause carcinoma in nonsmokers.
Some persons who don’t smoke can develop carcinoma after being exposed to asbestos, diesel exhaust, or other pollutants at work.
A small percentage of lung cancers arise in patients who have no known risk factors. Some of them could just be random events with no external source, while others could be the result of unknown influences.
Lung cancers in nonsmokers are frequently distinct from those that occur in smokers. They grow in younger persons and frequently have gene modifications that differ from those observed in cancers detected in smokers.
These gene variations can be utilized to guide treatment in some circumstances.
GENES CHANGES THAT MAY LEAD TO LUNG CANCER- Scientists have figured out how some lung cancer risk factors can cause DNA mutations in lung cells.
These modifications may result in aberrant cell development and, in some cases, cancer. Our genes, which determine how our cells work, are made from DNA, a cloth found in our cells. Our DNA, which comes from both parents, has an impact on more than simply our appearance.
It can also increase our chances of contracting certain diseases, such as cancer.
Some genes play a role in determining when cells divide, grow, and die:
Oncogenes are genes that help cells grow, proliferate, or survive.
Tumor suppressor genes help control cell division or induce cells to die at the appropriate moment.
DNA alterations that turn on oncogenes or turn off tumor suppressor genes can cause cancer. Lung cancer is frequently caused by changes in many distinct genes.
TYPES OF LUNGS CANCER
There are 2 main sorts of lung cancer:
NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER(NSCLC)-
NSCLC accounts for about 80% to 85% of lung cancer cases. Adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and giant cell carcinoma are the three primary subtypes of NSCLC.
Because their therapy and prognoses (outlook) are typically similar, these subtypes, which start from distinct types of lung cells, are classed together as NSCLC.
Adenocarcinoma: Adenocarcinomas begin in cells that ordinarily release mucus or other substances. This type of carcinoma is commonest in those that smoke or have smoked within the past, but it’s also the foremost common sort of carcinoma detected in nonsmokers.
It affects more women than males, and it’s more common in younger individuals than other sorts of carcinoma.
Adenocarcinoma is most commonly detected in the lungs’ outer layers, and it is more likely to be discovered before it has spread.
People with adenocarcinoma in situ (formerly called bronchioloalveolar carcinoma), a kind of adenocarcinoma, have a better prognosis than those with other types of lung cancer.
Squamous cell carcinomas begin in squamous cells, which are flat cells that line the liner of the lungs’ airways. They are usually seen within the middle region of the lungs, near a main airway, and are associated to a history of smoking (bronchus)
Large cell carcinoma, also known as undifferentiated carcinoma, can develop in any area of the lungs. It has a tendency to spread and grow quickly, making treatment more difficult. Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma, a subtype of huge cell carcinoma, may be a fast-growing malignancy that’s remarkably almost like small cell carcinoma.
Other subtypes: Adenosquamous carcinoma and sarcomatoid carcinoma are two other NSCLC subtypes that are far less common.
SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER(SCLC)-
SCLC is a type of lung cancer that accounts for 10% to 15% of all lung malignancies and is also known as oat cell cancer.
This kind of lung cancer grows and spreads more quickly than NSCLC. At the time of diagnosis, almost 70% of those with SCLC will have cancer that has already spread.
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy work well for this cancer because it grows quickly. Unfortunately, the cancer will return for the majority of patients at some point.